Electric vehicles and charging
Electric vehicles (EV) represent opportunity to change the way Queenslanders travel and use electricity.
Charging your EV
There are 3 main ways (or levels) to charge your EV. The charging time and range may vary depending on the vehicle.
Level 1 – Slow charge
- commonly used in homes to ‘top up’ daily use of EVs
- lower-cost depending on tariff and time of day
- uses an existing power point with an EV charging cable
- provides a 10 to 20km range for every hour of charge
- charging overnight or during the day for a few hours outside peak demand will generally give you 100-200km range.
Level 2 – Fast charge
- more likely to be installed in homes, apartment complexes, workplaces, shopping centres, hotels, etc. – where the vehicle will be parked for longer periods
- requires a dedicated wall mounted AC EV charger of between 7kW and 22kW. Provides between 40 to 100km per hour of charging depending on the EV and size of charger
- check specific installation connection requirements and tariff options with your local distribution network service provider (Energex or Ergon Energy).
Level 3 – Rapid charge
- used at commercial charging locations such as service stations and roadside locations like the Queensland's Electric Super Highway
- uses dedicated DC EV charger from 25kW to 350kW
- at the lower end can provide up to 150km per hour of charging.
Standard charging plugs
Type 2 (Mennekes) plug for alternate current (AC) charging
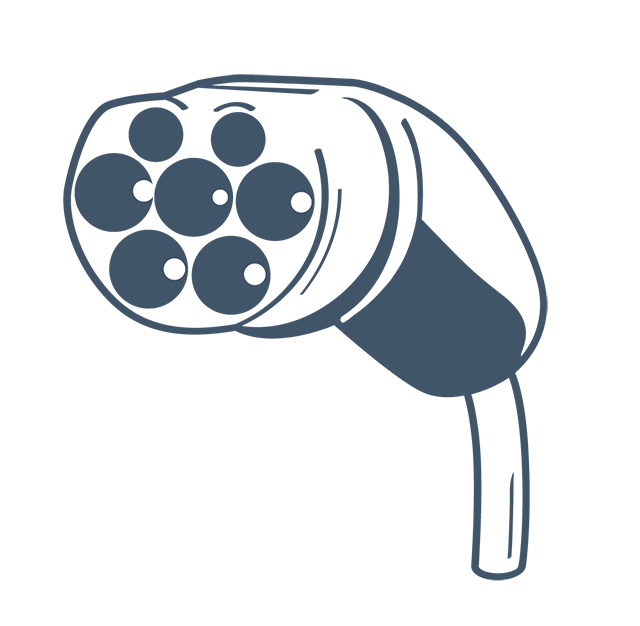
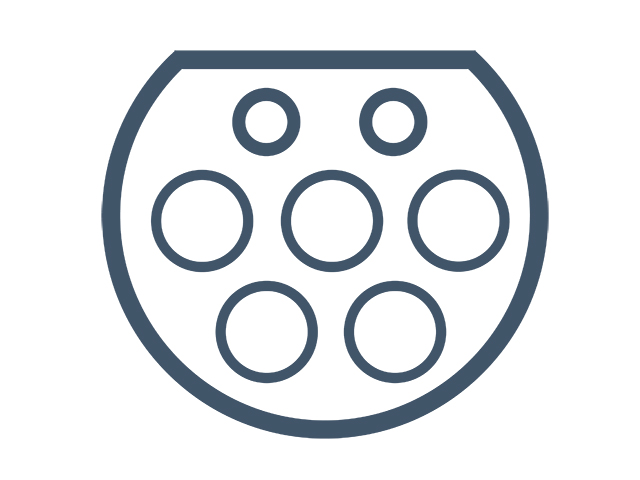
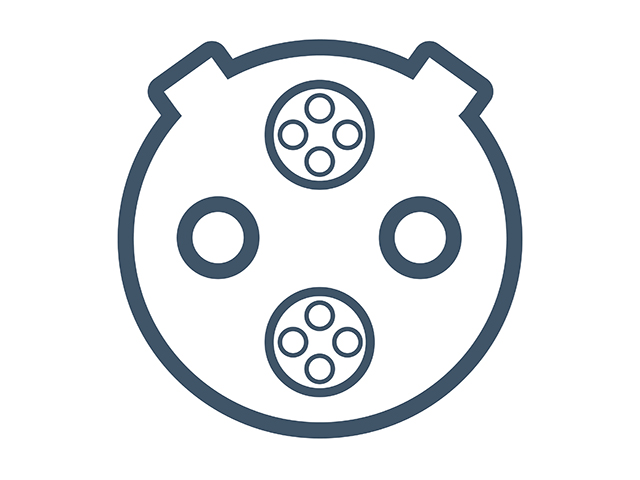
Combined charging system (CCS2) for direct current (DC) charging
CCS2 is becoming the standard DC plug type. All new EVs sold in Australia will have both the AC and DC plugs as standard.
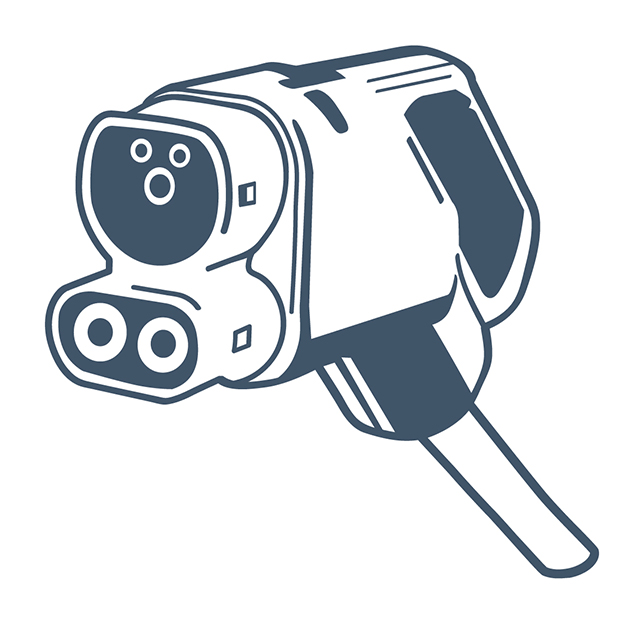
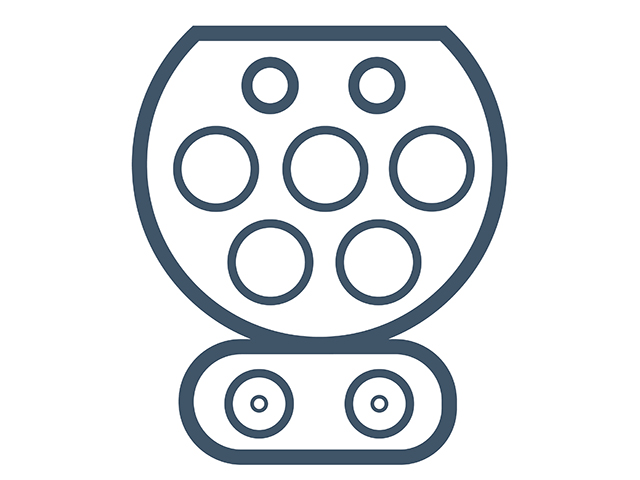
Charge de move (CHAdeMO) for DC charging

Best time to charge your EV at home
Charging EVs during off-peak hours (between 9am and 4pm) helps soak up excess renewable energy that is produced during the day and takes pressure off the energy system during peak times. This helps the electricity system operate more efficiently.
Read how daytime charging can help reduce the costs of electricity for households.
Battery reliability and warranties
Most vehicle manufacturer warranties for batteries are 8 years or 160,000km. If the battery drops under 70% of its original capacity, it may be replaced under warranty.
EV batteries may lose 2–3% of their original capacity for the first few years and then level off. A 10 year old car is expected to have at least 70% of its original capacity and many EVs still have 80–90% battery capacity. Current EV batteries are expected to outlast the rest of the vehicle..
Potential EV owners should investigate EV battery warranty and serviceability with the vehicle manufacturer before buying.
Battery lifecycle
We are developing the Queensland Battery Industry Strategy to support the transition to a low-carbon future.
When a battery is removed from the vehicle, the battery may be used as stationary storage, such as a home or community batteries.
Read how EV batteries can be used to power your home.
Battery safety
All EVs tested in the last 5 years have received a 5-star safety rating from the Australian New Car Assessment Program (ANCAP) before being released to the public.
Read about EV safety from Queensland Fire and Emergency Services.


